Lower back pain is just a symptom, an external manifestation of some disease or pathology.Any pain has its own reason.There are many causes of back pain.
Patients are often told that back pain is caused by overloading the muscles and ligaments.Unfortunately, if the cause was only in the muscles, it would be very easy to relieve the pain.For example, a massage which should provide relief.But massage doesn't always help because it removes the cause of the pain.
Herniated disc or disc bulge can cause severe back pain.If the disc herniation is on the right side, you may experience right back pain, pain in the right side, or pain in the right leg (sciatica with a large hernia).If the hernia is on the left side, you may feel back pain on the left side, and the pain on the left side may bother you.
If the hernia is large and presses on the left lumbar root (radiculitisOn the left side), then lumbago may occur in the left leg and pain may begin in the left leg.A large hernia often causes a violation of posture in the form of deformity of the torso with intense "twisting" pain, when it is impossible to straighten and straighten (the so-called antalgic position of the torso).
Lower right back pain may be caused by herniation or deformity of the right joints of the spine, or the sacral region (right iliosacral joint).
Pain in the area of the left shoulder blade (or pain under the left shoulder blade) may be the result of either a hernia or joint deformity, or may result from heart problems.Such pain can be caused by angina pectoris and heart attack.Pain between the shoulder blades occurs not only with pathologies of the spine and osteochondrosis, but also with diseases of the stomach (gastritis, ulcers, cancer, etc.) and often intestines.
Cholecystitis and cholelithiasis often cause back pain on the right side and pain under the right shoulder blade.Gallbladder pathology often manifests as pain under the right rib.Diagnosis is required.
bumpDisc, are often incidental findings on MRI, whichcan doproceed without pain,disc herniation– This is not a common cause of severe back pain.However, hernia formation, for example when lifting heavy objects, causes lumbar or thoracic lumbago (severe back pain).In the case of persistent back pain, the hernia found in the MRI may have nothing to do with it.The causes of this type of persistent pain often vary. Diagnostics will help you find out.
Therefore, to effectively treat back and lower back pain, you must:
- Determine the cause of low back pain (establish a diagnosis).
- The cause of low back pain will be determined by a neurologist, an orthopedic traumatologist with skills in the field of vertebrology and vertebroneurology, or a vertebrologist (vertebroneurologist).The diagnosis is established using clinical and hardware testing.
- Treatment strategy for low back pain depending on the diagnosed cause.
- If you have lower back pain, it is important to ensure that the pain does not recur.To achieve this, we offer a variety of methods, including spinal physical rehabilitation.
lower back pain.Why does my lower back hurt?
Low back pain refers to pain that is localized in the area between the 12th pair of ribs and the gluteal folds.This kind of pain is already a social problem.The fact is that the lower back is the most loaded part of the spine, experiencing greater loads daily and hourly.85% of people have experienced pain in the waist area at least once in their lives.What is the reason?
pain in waist areaThere could be many reasons.The most common causes are osteochondrosis, herniated discs, radiculitis and deformities of the lumbar joints.
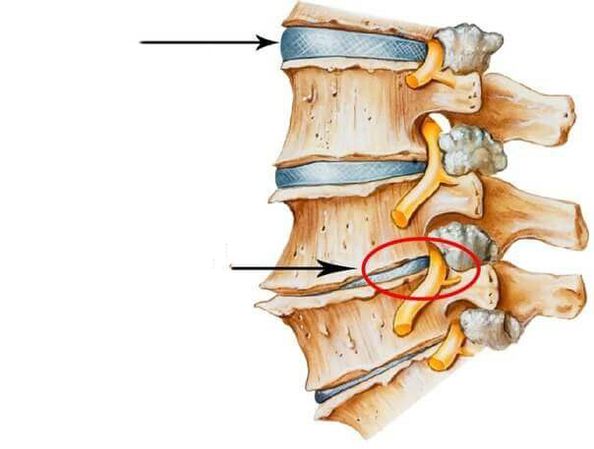
osteochondrosis
osteochondrosis,Natural aging of spinal cord tissue.
It is generally accepted that osteochondrosis is a sign of a disease of the spine, which is accompanied by pain.This is a little different.
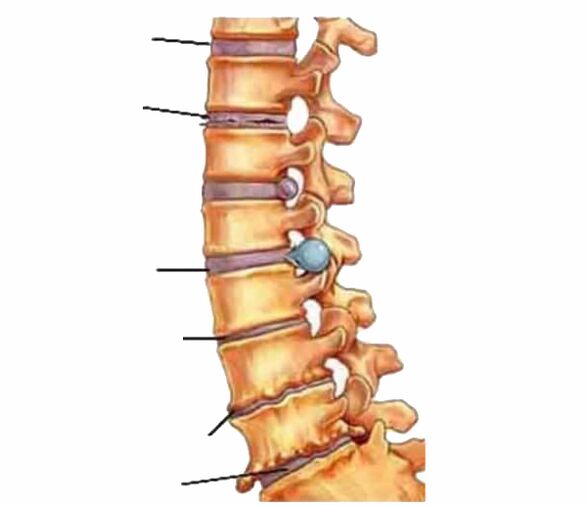
The picture below shows a normal disk being damaged (see damaged disk in the picture).These damages can accelerate the aging of the disc and reduce its height (see "Narrowing of the intervertebral space").Subsequently, aging begins to affect the bone tissue of the vertebrae themselves and osteophytes begin to grow (see "Osteophytes" in the diagram).
Previously, it was believed that osteochondrosis was associated with pain.Therefore, at that time they tried to explain the cause of pain in the spine and lower back specifically with osteochondrosis.For this reason, the question of failure of vertebroneurology also arose.In 1978, the first research laboratory for the problems of spinal osteochondrosis was created, which studied the issue of osteochondrosis for more than 10 years and proved that the cause of pain is not osteochondrosis, but joint pathology.
Osteochondrosis does not cause pain because the disc has no nerve endings.Therefore, there is no pain with osteochondrosis.
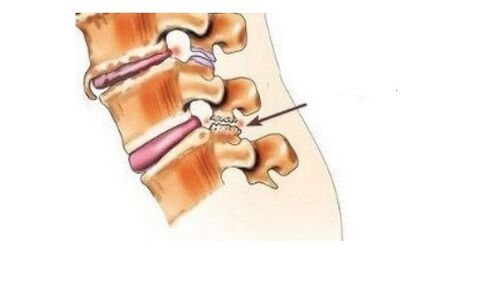
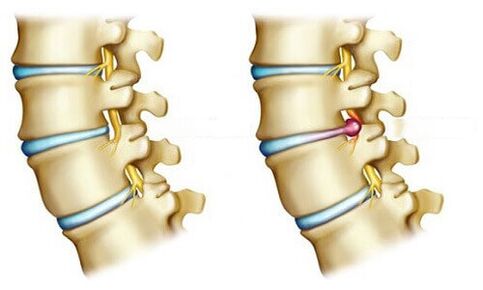
disc herniation
Disc herniation as a possible cause of pain.The picture above shows multiple disc herniations – a small herniation (protrusion) and a large disc herniation.The herniated disc itself does not cause pain.
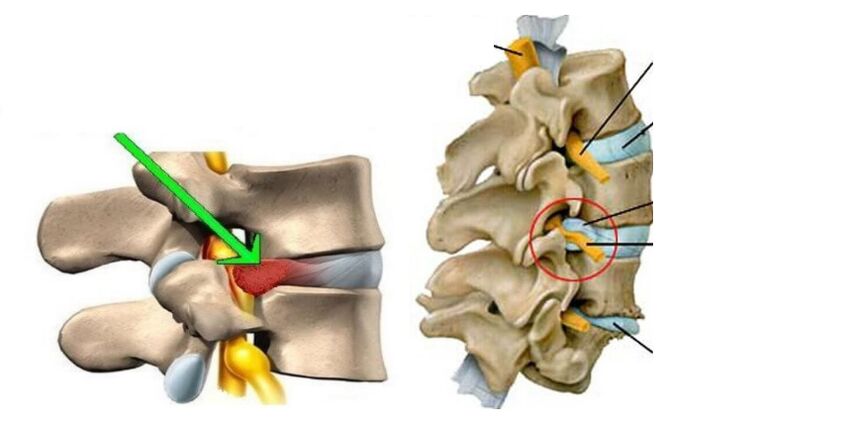
The disc has no nerve endings (not embedded).Pain from a disc herniation or bulge occurs when the hernial bulge puts pressure on the internal tissue.For example, onspinal cordor onBackyuyulongitudinalWow!bundleBut,In the first case, radicular pain occurs - radiculitis (see below).In the second, when the receptors of the posterior longitudinal ligament are irritated, back pain (lambodynia) or intense pain - lumbago (lumbago) appears.
Herniated discs can often be treated without surgery.
spondyloarthrosis
Spondyloarthrosis is arthrosis of the joints of the spine.Arthrosis is characterized by a disease of the cartilage of the joints themselves.In this case, the cartilage decreases in height (degenerates, "dries up"), and the articular surfaces of the bone lose their protective cartilage layer.Pain starts in the joints of the spine.This pain feels like pain in the lower back.
radiculitis
Radiculitis is an inflammation of the root.Radiculitis often occurs when the root is injured by a herniated disc or spinal joints.This is usually not as much lower back pain as pain in the legs, buttocks, and even pain or numbness in the toes.
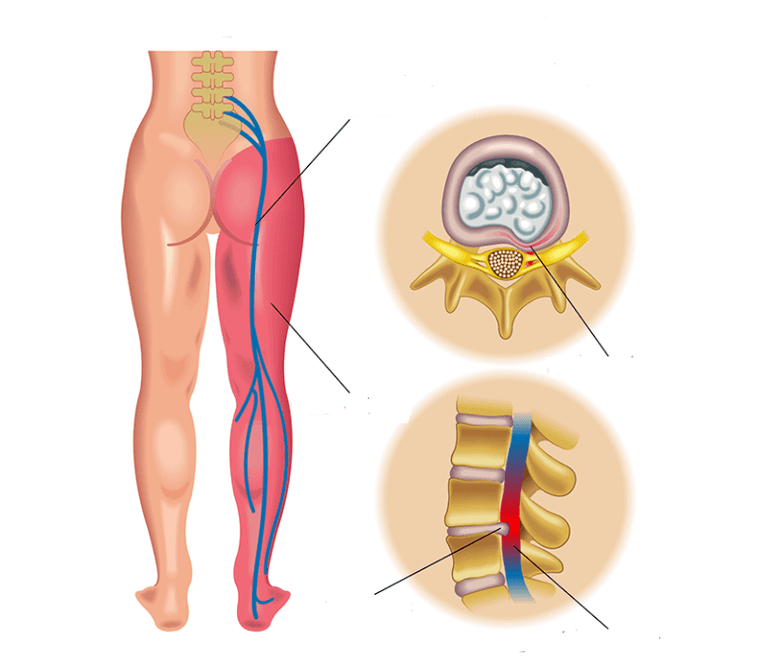
Radiculitis is treated most effectively by freeing the root.If it has arisen due to disc herniation, you need to reduce the hernia, which puts pressure on the root.
Pain in the back and lower back due to deformity of internal organs
Back pain is possible due to pathology of internal organs.For example,lower back pain in womenMay be the result of diseases of the pelvic organs.
lower back pain in women
Lower back pain in women can be caused by inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs.
If a woman has pain in the pelvis and lower back, you should always remember about gynecology.Inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs are not uncommon.Its cause can be inflammation of the appendages, inflammatory diseases of the vagina and vulva, salpingitis, salpingophoritis, endometritis, bacterial vaginitis, etc.Often, such inflammatory diseases in women are caused by infections of the genital area, including sexually transmitted infections.
If there is pain and ache in the lower back, as well as pain in the lower abdomen, the woman should be examined by a gynecologist.Initially it is mandatory to undergo gynecological ultrasound to clarify the diagnosis.
Constant nagging pain in the lower back also occurs whenOncology in Gynecology,
Cancer and lower back pain in women
Cancer does not cause pain in the beginning,When pain appears in the lower back or sacral region, it is already too late.
Many people think that tumors also cause pain.This is wrong.In the early stages of tumor development, a person does not feel pain.The person feels practically healthy.For example, cervical cancer in the genital organs is asymptomatic.It begins to manifest itself as the tumor grows.In this case, pain often appears in the lower back and lower back.There is pain in the sacrum area below the lower back.
With cancer, severe lower back pain may not bother you initially.Rather, there is no pain in the lower back, but pain.Such pain can be the first call that will help a woman stop the serious growth of the tumor and make the correct diagnosis in time.If there is persistent pain in the lower back or sacrum, you should pay special attention to it so as not to miss a disaster.
Unfortunately, if you ignore lower back pain or discomfort, the next sign of cervical cancer may be uterine bleeding.This is the stage at which the tumor begins to disintegrate, when metastases may already have occurred.Including in the spine, when there is already severe pain in the lower back.
Important measures:If your lower back hurts, it is not necessarily osteochondrosis or a herniated disc.And taking preventive consultation from a gynecologist never hurts.After all, cervical erosion found during examination is a precancerous condition.
Why do urinary or urogenital problems (inflammation) cause my back pain?
Acute lower back pain may be caused by kidney disease
Kidney diseases like pyelonephritis cause severe lower back pain.
Pyelonephritis is an infectious disease, often caused by progressive infection.It may be related to sexually transmitted infections and other types of household infections transmitted through swimming pools, bathrooms and personal hygiene items.For example, everything stays in the towel for a long time without being washed.
Inflammation activates pain receptors in the soft tissues of the pelvic organs.The pain signal (impulse) reaches the spine through sensitive roots, and activates its tissues.The soft tissues of the spinal cord and the attachment points of the back muscles become reflexively swollen.And my lower back starts hurting.
Persistent back and lower back pain due to dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract and other diseases
With intestinal cramps, with inflammation, with ulcers or ulcerative colitis, with stomach ulcers and gastritis, the back usually hurts.
stomach cancer associated with back pain
Pain caused by pathology of the gastrointestinal tract will not improve with back treatment.It is necessary to treat the cause.
Another possible cause of lower back pain is overloading the back.
Excessive load on the lower back is a common cause of back pain or its aggravation.Overload often affects the joints of the low back, ligaments, tendons or muscles of the low back.In addition, the muscles of the lower back work actively under load.Therefore, if you have spinal pain in the waist area after exercise, it is not necessarily a disease.This could be a muscle tear.If this pain does not go away within 1-2 days, you should think about problems with the lumbar spine.Especially if this pain increases with movement.
The cause of such pain is often overloaded inflammation of the muscles and their attachments.Or - inflammation of the joint capsule.
If such intensity occurs more than once a year, you should look for the cause of such intensity.To do this, it is not enough just to consult a doctor and do manipulations, painkillers, massage and other procedures.
Such recurring pain requires an examination to determine the cause.
soft tissue injury in the lower back
Severe pain in the lower back when walking awkwardly or lifting a heavy object is most likely due to a spinal cord injury.
If you are concerned about pain on that side, for example, lower back pain on the right side, you should think about the deformity of the joint located on the right side.Or about hernia of the right side of the lumbar spine.
Types of lower back pain
Pain, regardless of duration, can be acute, long-term, or have a (passing) transient character.
The pains are as follows:
- local pain- Pain especially in the lower back.
- referred pain- When the pain occurs not only in the lower back, but also in the buttocks, pelvic area, for example.Or, lower back pain occurs due to pathology of internal organs.In such cases they talk about referred pain.
- radicular pain- vary in significant intensity, and are localized within the boundaries of the root transition (from the spine to the periphery).Its cause is infringement (stretching, compression, curvature, compression) of the nerve root of the spinal cord.Pain increases with movement or even coughingcoughing fit,This is severe pain in the lower back that can spread to the leg.
- myofascial pain- Resulting in reflex muscle spasm.Myofascial pain can be caused by diseases of internal organs or damage to the spinal cord.Muscle spasms significantly disrupt the biomechanics of human movements.Chronic muscle spasms can also cause back pain and cramps.
In what cases should you consult a doctor for lower back pain and what to do?
- With sharp (intense) pain in the lumbar region;
- If back or lower back pain persists for more than 3 days;
- If back pain appears after an injury;
- If the pain is localized simultaneously in the lower back, leg and lower leg;
- If pain in the lumbar region is associated with numbness in the thigh, buttocks, leg, foot, waist;
- If pain in the lumbar region is accompanied by torsion (attraction) of the muscles of the limbs;
- If the function of urination and defecation is impaired (urinary retention, incontinence, frequent urination or false urge to urinate);
- If the perineum is numb.
- If the pain in the back or lower back (sacrum) is persistent, worse in the morning
What to do if you have lower back pain?
The causes of low back pain vary, so treatment of low back pain should only be done after diagnosis and by a qualified physician.Any pain in the vertebral region requires medical examination and clarification of the reason for its occurrence.
There are 3 purposes for visiting a doctor:
- Establish the correct diagnosis.
- Relieve the pain.
- Formulate measures that will help maintain the patient's health so that the pain does not recur.
Possible causes of lower back pain
The following diseases may be the reason for your complaint of lower back pain:
- Osteochondrosis;
- osteoarthritis,
- spondylolisthesis,
- spondylosis,
- Swelling of the joints of the spine,
- spondyloarthropathy,
- muscle damage,
- ligament damage,
- disc herniation ,herniaDiscs are treated without surgery in 98% of cases (world statistics)",
- Atherosclerosis of the abdominal aorta;
- Malignant neoplasm of spinal cord,
- spinal metastases,
- urinary tract infections,
- spinal stenosis;
- biliary tract diseases,
- penetrating duodenal ulcer,
- pancreatitis,
- kidney disease,
- Dissecting aneurysm of the abdominal aorta;
- Hemorrhage into retroperitoneal tissue,
- Inflammatory diseases of female genital organs,
- Oncological diseases of female genital organs,
- endometriosis,
- prostatitis,
- prostate cancer,
- epithelial cerebellar duct abscess,
- embolism of arteries of lower limbs,
- intermittent claudication,
- pseudo-intermittent claudication,
- elimination of atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities;
- rheumatoid spondylitis,
- polymyalgia rheumatica,
- fibromyalgia
- Depression,
- Other.
Treatment of lower back pain (back pain)
At the stage of initial treatment of pain in the lower back (back), a primary diagnosis is established.This is done on the basis of a survey, medical history, neurological and orthopedic examinations.At this stage, medications may be prescribed to reduce pain, relieve tissue swelling, and general anti-inflammatory therapy.Reflexology, local medicinal effects, regional anesthesia, various injection methods, laser therapy, etc. are effective for the treatment of lower back pain.In acute and subacute periods, rest is important during drug therapy.Physiotherapy, massage, manual therapy, which can aggravate the process, are not indicated.In the acute period, traction is also not used: hardware, on inclined boards, on wall bars.
To treat low back pain more effectively, you need to understand its cause.For this purpose, the patient is further examined to clarify the diagnosis.There can be many reasons for pain in the waist area.An indicative list of diseases accompanied by lower back pain is listed above.Each of them has its own treatment protocol with the most effective approaches, list of drugs and procedures.The protocol also includes data on methods not indicated for this disease.For example, for inflammatory diseases of the spine (spondylitis, spondyloarthropathy, spondyloarthritis, myositis, ligamentitis, etc.), manual therapy, massage and physiotherapy are not indicated due to ineffectiveness and the risk of complications.It is important to identify the cause of swelling and treat it.
Spondylosis visible on radiographs may occur without clinical symptoms and can often lead to more complex disease.Therefore, treating spondylosis is useless and often dangerous: removing bone growths in the spine is not realistic, and there is no need.The patient faces exotic diagnoses like "muscle damage", "muscle spasm", "ligament damage".may have to.Unfortunately, it is not always true to talk about muscle cramps as a cause of pain.Muscle spasms of the paravertebral muscles are a reflex action and, as a rule, accompany most diseases, including those not related to the spine.The muscles are actively involved in the segmental reflex process and can respond to any irritation both in the spine and outside it.The so-called "cramps" should be differentiated from reflected or projecting pain in the lower back, which can be caused by the pathology of internal organs: diseases of the pelvic organs, retroperitoneal space, kidneys, pancreas and prostate glands, gynecological diseases of inflammatory or tumor origin, diseases of the aorta, hemorrhages in the retroperitoneal tissue, and much more.Osteopathic techniques of working with the secondary spasmodic paravertebral muscles, at a reflex level, can temporarily alleviate the condition.For example, manual therapy, osteopathic techniques, inclined boards, massage, traction, physiotherapy will not help with prostatitis or adenomatosis.So-called "medical removal".The "muscle cramps" in this case are simply the manipulator's desires.
Treatment of hernia and disc bulge in lower back
Often, an MRI reveals a hernia or bulge, which is thought to be the cause of low back pain.The question immediately arises: remove the hernia or try to deal with it without surgery?
first thing to do- Explain how important this hernia is from medical point of view.The fact is that if you take 100 absolutely healthy people without lower back pain and do MRI diagnostics, it turns out that 80% of them have some kind of disc protrusion ("hernia"), which does not give any symptoms.
Often, disc herniation may be an incidental finding, often attributed to some other cause of pain.
At the same time, practice shows that not all hernias are clinically significant.To clarify the causes of pain, a thorough medical history is taken, a neurological examination is performed to identify neurological deficits, clarify the functioning of the pelvic organs, etc.
It turns out that not all hernias and disc bulges require surgery.The number of patients who require such operations does not exceed 2%.
Neurosurgeons have set absolute indications for surgery, which are clearly defined.Often, the presence of a disc herniation is not a reason for emergency surgery.
There is a sufficient arsenal for the treatment of disc herniation and bulge, which includes traction, creation of stable motor patterns in the back, local and general drug therapy methods, physiotherapy, reflexology, etc.Calibrated treatment without surgical intervention is often accompanied by regression of symptoms, and the hernia (protrusion) may reduce over time.
When deciding on surgery, one should take into account the relative indicators of surgical treatment, which are officially determined by neurosurgeons.Each specific case is considered separately, taking into account clinical symptoms, medical history, anamnesis, neurological and orthopedic examinations, the results of hardware and laboratory examinations.
It should be especially noted that surgical intervention is often associated with a number of complications, which have to be dealt with after surgery with pain relief several times more intensively than before surgery.
Degenerative changes in the spine, such as osteochondrosis, spondyloarthrosis, spondylosis, etc., are treated depending on the identification of the trigger of the pain syndrome.
Massage and manual therapy are quite effective methods of treatment if there are indications for their use.Over the past three decades, the Institute has developed optimal protocols for the management of patients with low back pain taking into account the potential range of their causes.



















































